What is public cloud? It’s a model of cloud computing where infrastructure and services are delivered over the internet by third-party providers, available to anyone who needs them. Whether you’re a startup launching your first app or an enterprise scaling global operations, the public cloud has become the default foundation for flexible, on-demand IT resources.
| “Cloud isn’t just about where you run your workloads—it’s about who you trust to run them. The right public cloud gives you performance, transparency, and control on your terms.” |
In this blog, we’ll break down what the public cloud is, how it works, and why it continues to shape the way businesses think about infrastructure.
Understanding Public Cloud Computing
The global public cloud market is projected to reach $723.42 billion in 2025. Public cloud is built on the idea of shared access to computing resources—without the need to invest in or manage physical hardware. Instead of maintaining their own servers, organizations use infrastructure hosted and managed by an external provider.
Key Characteristics
What sets a public cloud apart from other models?
- Multi-tenant architecture: Multiple users share the same infrastructure, with logical separation for security and privacy.
- Elastic capacity: Resources can scale instantly to match demand.
- Metered billing: Users only pay for what they consume.
- Provider-managed infrastructure: Hardware, maintenance, and uptime are handled by the provider.
These traits make public cloud infrastructure a popular choice for businesses that need flexibility, fast deployment, or global reach.
A Growing Ecosystem
96% of companies use at least one public cloud. While AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud are the most well-known names, they’re not the only ones.
Many businesses look to providers who offer:
- Specialized performance capabilities
- Control over their data, systems, and tools
- More predictable pricing or personalized support
For companies with specific performance, security, or support expectations, the right public cloud partner isn’t always the biggest—it’s the one that aligns best with their workload and priorities
More insights from The Sharktech blog: |
How Public Cloud Works
Public cloud operates on a provider-owned infrastructure model. That means the hardware—servers, storage systems, networking components—is maintained entirely by the cloud provider. Users access these resources remotely through the internet, typically through a web portal, API, or developer tools.
Behind the Scenes
Here’s what happens when you use public cloud services:
- Your applications and data are hosted in a remote data center.
- You choose the level of performance and resources (e.g., CPU, RAM, bandwidth) based on your workload needs.
- The provider handles uptime, physical security, hardware updates, and capacity planning.
From the user’s perspective, it feels like you’re spinning up resources with a few clicks, but under the hood, it’s a complex orchestration of virtual machines, storage volumes, load balancers, and more.
Public Cloud Service Delivery Models
Public cloud supports a range of use cases, from app hosting to data storage. While this blog focuses on the infrastructure model, it’s helpful to know the three layers of service commonly delivered:
Service Model |
Description |
Example Use |
| IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) | Raw computing resources like VMs, storage, and networking | Hosting websites, running databases |
| PaaS (Platform as a Service) | Development environments and tools on top of IaaS | Building and testing applications |
| SaaS (Software as a Service) | Fully managed software accessible via browser or API | Email, CRMs, collaboration tools |
These models help users choose the right level of control, management, and scalability depending on their goals.
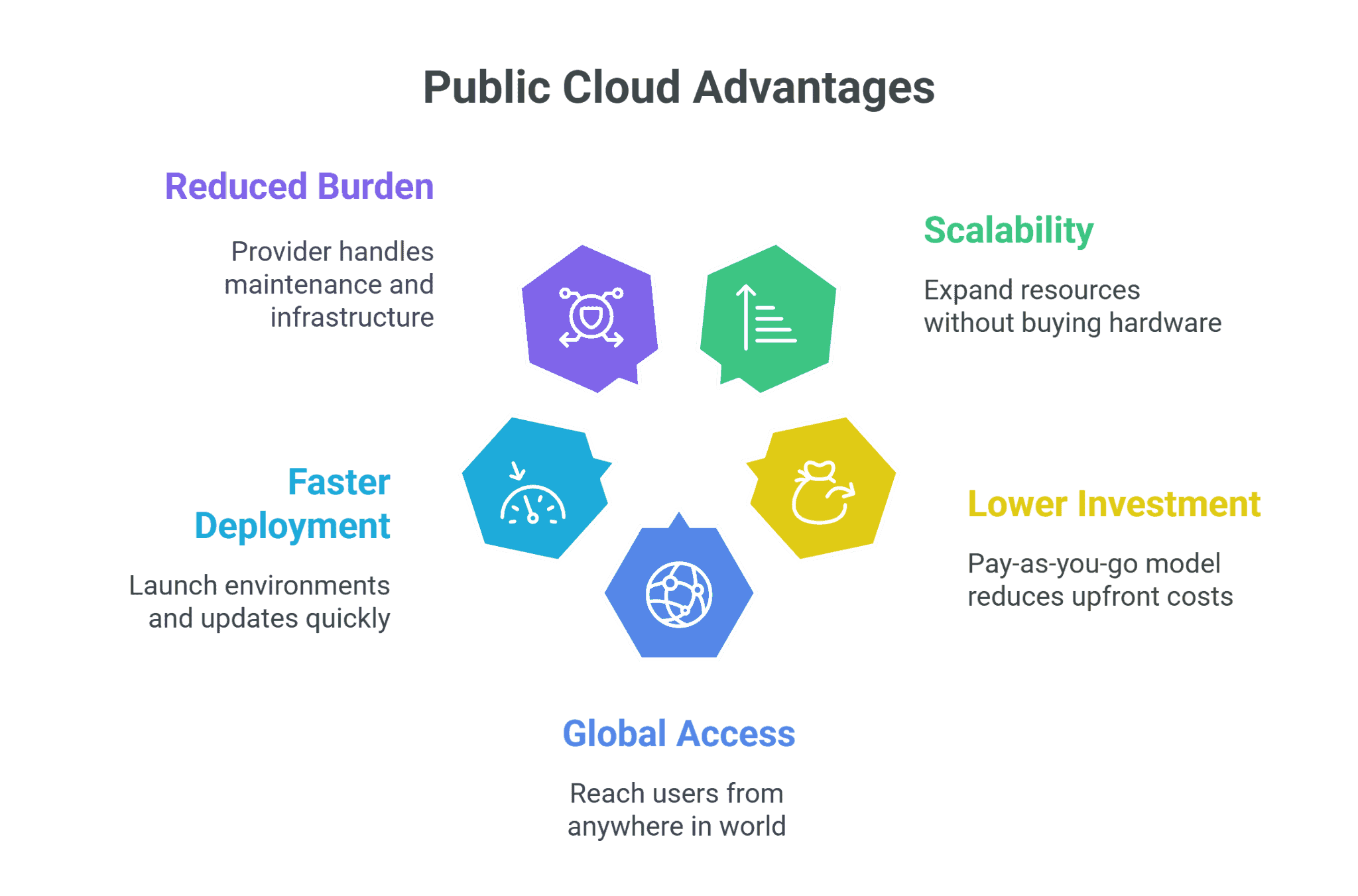
Benefits of Public Cloud
Public cloud has become a practical choice for many organizations because it removes the challenges that typically come with private infrastructure. Teams can launch applications, run workloads, or test ideas without waiting on hardware procurement or complex setup. It’s flexible, accessible from anywhere, and makes it easier to manage costs as needs change.
Here are some of the most widely recognized advantages:
Why Organizations Choose Public Cloud
-
Scalability without friction
Quickly expand or reduce resources to meet changing demand, without the delays or costs of buying new hardware.
-
Lower upfront investment
Shift from capital expenditures (CapEx) to operational expenditures (OpEx), paying only for what you use.
-
Global accessibility
Deploy services and reach users from anywhere with an internet connection, regardless of geography.
-
Faster time to deployment
Launch new environments, test applications, or roll out updates in minutes instead of weeks.
-
Reduced infrastructure burden
Let the provider handle hardware, maintenance, and uptime—freeing up your team to focus on applications, not servers.
More Than Convenience
Beyond the obvious benefits, some organizations choose a public cloud for greater transparency and resilience.
For example:
-
Transparent pricing and cost control
Some providers offer fixed pricing, billing visibility, or tools to forecast and manage spend more predictably.
-
Built-in protections
Security features like DDoS mitigation, traffic monitoring, and encrypted storage are often integrated at the platform level.
-
Hands-on support
Instead of ticket-based systems or chatbots, some public cloud providers prioritize real-time support from actual infrastructure experts.
Is public cloud only for the giants?AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud aren’t your only options. Their platforms offer scale—but pricing can be complex, unpredictable, and hard to manage. The Sharktech Cloud gives you flexible infrastructure with transparent costs and direct support, so you’re never guessing what your next bill will look like. |
Examples of Public Cloud Platforms
The public cloud ecosystem includes a range of providers—some with massive global reach, others built for simpler, more focused infrastructure delivery. Here are a few of the most widely used public cloud platforms:
-
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
The largest public cloud provider, offering extensive services for compute, public cloud storage, networking, analytics, machine learning, and more. Known for scalability and breadth, but often criticized for complex pricing.
-
Microsoft Azure
A strong choice for organizations already using Microsoft products. Offers a broad range of services, enterprise integrations, and hybrid cloud support.
-
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Popular for data analytics, machine learning, and Kubernetes support. Integrates closely with other Google services and emphasizes open-source tools.
-
IBM Cloud
Combines public cloud infrastructure with AI, hybrid cloud, and enterprise security features. Often used in regulated industries or by legacy enterprise systems.
-
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)
Focuses on high-performance compute, enterprise workloads, and database hosting. Commonly used by companies running Oracle software stacks.
-
The Sharktech Cloud
A public cloud platform focused on simplicity, transparency, and control. Offers flexible infrastructure with direct access to support and predictable pricing—without the layers of hyperscale complexity.
When Public Cloud Makes The Most Sense
47% of companies are pursuing a cloud-first strategy. Public cloud is designed for adaptability. It’s especially well-suited for teams that need to move quickly, respond to change, or scale without committing to long-term infrastructure investments.
These are some of the most common use cases where public cloud delivers clear value:
🚀 Fast Deployment for StartupsEarly-stage teams often don’t have the time or capital to invest in on-prem infrastructure. Public cloud allows them to launch quickly without contracts or complex setup. The focus stays on building, not managing servers. |
📈 Scaling Production WorkloadsApps with fluctuating traffic, like SaaS platforms or client-facing services, benefit from the ability to scale resources up or down as needed. Public cloud helps maintain consistent performance during high and low usage periods. |
🧪 Development and TestingDev teams can quickly create environments for testing, QA, or sandboxing. Once testing is complete, resources can be shut down with no overhead or cleanup. |
🔄 Backup and Disaster RecoveryPublic cloud makes it easier to store backups offsite, replicate systems, and recover from outages. It’s a practical option for building resilience without managing a secondary facility. |
⚙️ High-Performance WorkloadsSome platforms offer infrastructure designed for compute-heavy or data-intensive tasks. This is ideal for running analytics, batch jobs, or media processing without hardware limitations. |
|
The Next Steps For Public Cloud
Public cloud has become a foundation for how businesses build and scale. As more platforms emerge beyond the Big Three, teams have real choices in how they approach cost, control, and support. The next step is choosing the platform that fits.
Explore The Sharktech Cloud to see how simple, transparent a public cloud can be.




More to Read
The OpenStack Public Cloud Complexity Problem (And Why It’s Costing You)
Choosing the right cloud platform today is akin to trying to pick a needle
Oct
Make Growth and Security Part of Your Public Cloud Management Strategy
Managing today’s cloud infrastructure is no longer just about spinning up servers or
Sep
Leading Cloud Service Providers Explained: Types, Benefits, and How to Choose
94% of businesses now use a cloud solution in some form. Whether it’s
Aug
What is Public Cloud? A Simple Guide For Businesses
What is public cloud? It’s a model of cloud computing where infrastructure and
Jul
What is Cloud Migration? A Practical Guide for Modern Businesses
What is cloud migration? It’s the process of moving digital assets—like data, applications,
Jul
Why Some Businesses Choose Self-Managed Cloud Instead
Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses deploy, manage, and scale their digital infrastructure.
Apr