In the ever-evolving landscape of web technologies, Content Delivery Network (CDN) has become a crucial component for enhancing the performance and reliability of websites.
Understanding the basics of CDNs is essential for website owners and developers seeking to optimize user experiences. Today, let’s dive into the fundamental aspects of CDNs and address the common question: Do I Need a CDN For My Website?
Do I Need A CDN For My Website?

The answer to whether you need a Content Delivery Network depends on the nature of your website and your goals for user experience. CDN offers several key benefits that can significantly improve your site’s performance.
Faster Loading Times
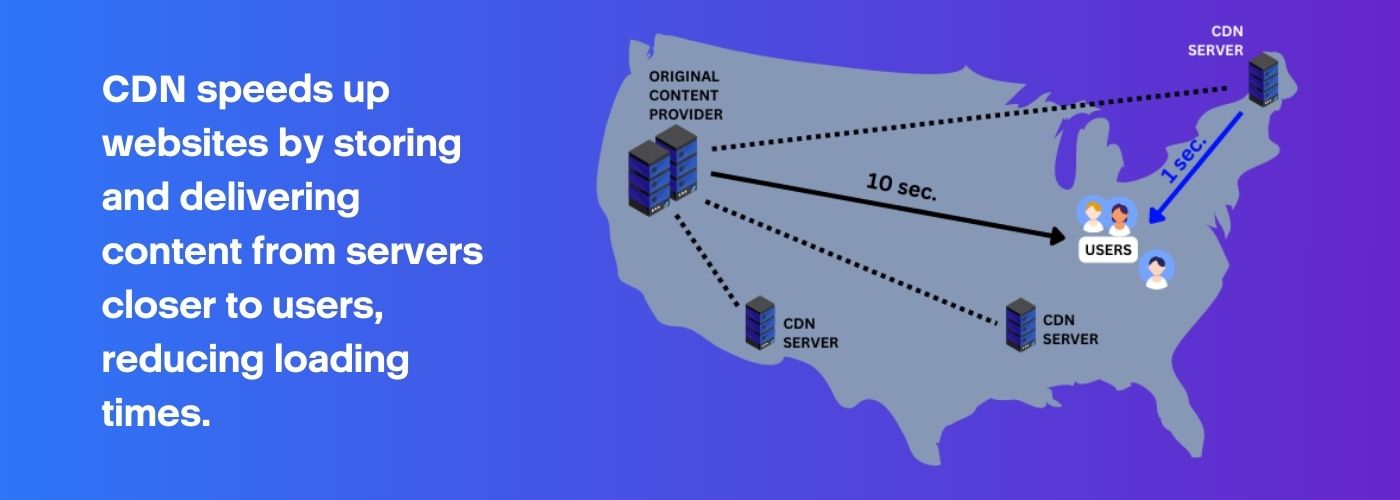
One of the primary advantages of using CDN is the acceleration of content delivery. CDN operates by distributing your website’s static content, such as images, stylesheets, and scripts, across multiple servers strategically located in various geographic locations. When a user accesses your website, the content is delivered from the server nearest to them, reducing latency and significantly improving page load times.
Global Reach
CDN becomes particularly valuable if your website caters to a global audience. Without CDN, users from different parts of the world may experience slower load times due to the physical distance between their location and your web server. CDN mitigates this issue by storing cached copies of your content in servers worldwide, ensuring a more consistent and speedy experience for users, regardless of their location.
Scalability and Reliability
CDN enhances the scalability and reliability of your website. By offloading the delivery of static content to distributed servers, CDN reduces the load on your origin server. This not only improves overall website performance but also ensures that your site can handle increased traffic without compromising on speed and responsiveness.
How CDN Improves Network Performance?
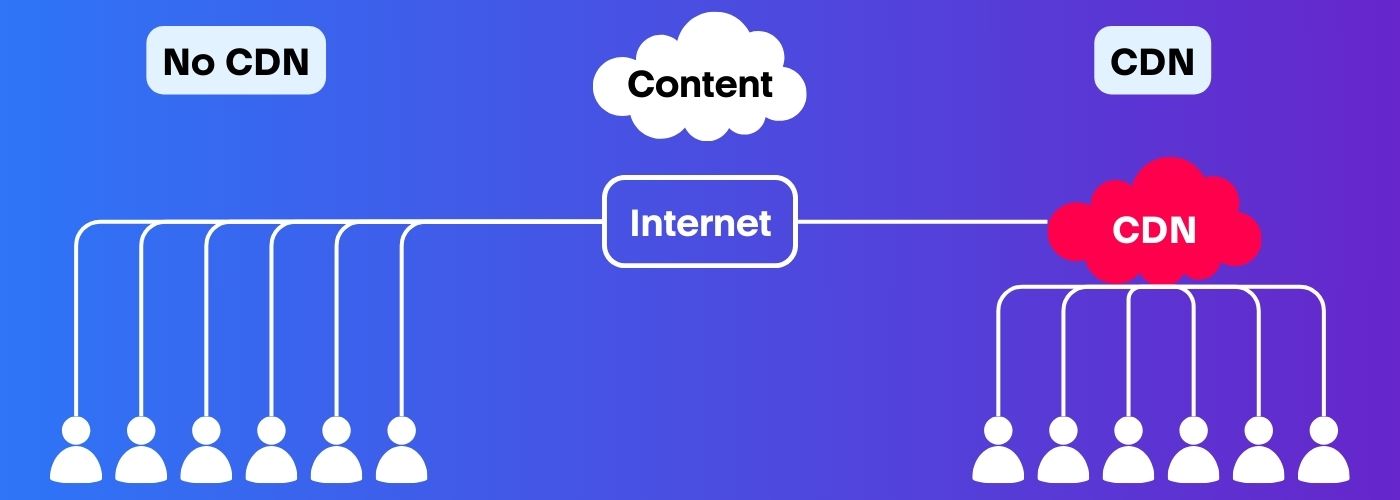
The Domain Name System (DNS) plays a crucial role in how CDN functions. When a user enters a website’s domain name in their browser, the DNS translates that domain into an IP address, directing the user to the server hosting the website. CDN integrates with DNS to optimize content delivery.
CDN uses caching to store static content in edge servers. When a user requests a particular piece of content, the CDN serves it from the nearest edge server instead of fetching it from the origin server. This reduces latency and accelerates content delivery.
CDNs implement load balancing to distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers. This ensures that no single server is overwhelmed, optimizing resource utilization and preventing bottlenecks that could impact performance.
CDN also often employs compression techniques to reduce the size of files transmitted over the network. Smaller file sizes result in faster load times, especially for users with slower internet connections.
How Does CDN Work With DNS?
The Domain Name System (DNS) plays a crucial role in how CDN functions. When a user enters a website’s domain name in their browser, the DNS translates that domain into an IP address, directing the user to the server hosting the website. CDN integrates with DNS to optimize content delivery.
Anycast DNS:
CDN typically uses Anycast DNS, a routing method that directs users to the nearest available server. This is achieved by broadcasting the same IP address from multiple locations. When a user makes a DNS request, they are directed to the closest server, reducing latency and improving load times.
CNAME Records:
CDNs often utilize CNAME (Canonical Name) records to map domain names to specific CDN endpoints. This allows for seamless integration of CDN services without requiring changes to the original domain configuration. When a user makes a request, the CDN’s DNS resolves the CNAME record and directs the user to the appropriate edge server.
Is A CDN Worth It?
The decision to invest in CDN depends on various factors, including the size and nature of your website, target audience, and performance goals. However, the advantages offered by CDNs make them a valuable asset for many websites.
While CDN service comes associated with a cost, the performance improvements it offers outweigh the expenses. Faster loading times, improved user experience, and the ability to handle increased traffic make CDN a cost-effective solution for websites of most scales.
CDN also provides an additional layer of security by offering features such as DDoS protection and web application firewalls. By filtering malicious traffic before it reaches your origin server, CDN can help neutralize IT security threats and improve your website’s security and reliability.
Search engines consider website speed as a factor when determining search rankings. By improving page load times, CDN can positively impact your website’s SEO, leading to higher visibility in search engine results.
For websites aiming to provide a fast and reliable experience to users across the globe, CDN proves to be a valuable investment, offering performance improvements, scalability, and enhanced security.


More to Read
What Are Managed Cloud Services? (And Why Some Businesses Choose Self-Managed Cloud Instead)
Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses deploy, manage, and scale their digital infrastructure.
Apr
How to Choose the Right Cloud Storage Solution: A Comparison of Features, Costs, and Security
The sheer volume of data businesses handle today is enormous. Globally, approximately 402.74 million
Apr
Sharktech Announces New Web Hosting and Cloud Industry Alliance
Sharktech and 22 Other Companies Launch Secure Hosting Alliance to Build Trusted Web Hosting Industry
Feb
Think the Cheapest Dedicated Server is A Good Idea? What You Need to Know
Should you hunt for the cheapest dedicated server? Finding the most affordable option
Oct
Discover How These 8 Cloud Monitoring Tools Can Help You Drive Better Business Performance
When it comes to managing your cloud environment, cloud monitoring tools are essential
Oct
Pick the Best Cloud Management Platform with These 5 Pro Tips
Managing cloud infrastructure can become overwhelming, especially as businesses scale and adopt more
Oct