94% of businesses now use a cloud solution in some form. Whether it’s to host their website, store back-up data, leverage third-party apps, or other uses, cloud technology is integral to modern business practices. Cloud service providers are behind this shift, making it possible for businesses to access computing power, storage, and tools easily, securely, and effectively.
| “Cloud service providers have changed how businesses grow. By removing the need for heavy upfront infrastructure investments, they’ve made it easier for companies to stay agile, scale on demand, and meet customers’ needs better,” said Tim Timrawi, CEO at Sharktech. “Most businesses don’t want to become experts in servers or networking, they just want their tools to work and scale as they grow. That’s exactly what the top cloud service providers make possible.” |
In this guide, we’ll break down what cloud service providers are, explore the different types of services they offer, outline their key benefits and challenges, and help you understand what to look for when choosing one.
What is a Cloud Service Provider?
A cloud service provider (CSP) is a company that offers access to computing resources like servers, storage, databases, and applications over the internet. Instead of setting up and managing physical hardware in-house, businesses can use a CSP to run their technology needs from a remote data center.
Cloud service companies maintain the infrastructure, handle security, and make sure systems stay online and up to date. Businesses, in turn, get access to the resources they need without the cost or complexity of managing everything themselves.
Some of the most widely known leading cloud providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. There are also many smaller or more specialized providers that focus on specific industries, support models, or performance needs.
Not all cloud providers offer the same services. Some focus on raw infrastructure, like virtual machines and cloud storage. Others offer platforms for developers to build and test applications, or ready-to-use software that runs entirely in the cloud.
For example:
- A startup might use AWS to run its website and store user data.
- A development team might use Google Cloud’s tools to build and deploy an app.
- An organization might rely on Microsoft 365, which runs on Azure, to handle email, document sharing, and team communication.
- A company with specific performance or configuration needs might work with an alternate cloud service company to host applications in a more controlled or cost-effective environment.
Different Types of Cloud Service Providers
Cloud service providers operate differently. Some are built for global scale and mass adoption. Others are designed for more specific use cases, like privacy, customization, or industry-specific needs.
Here are a few common categories of cloud server service providers, with examples to help illustrate each:
| Provider Type | Description | Examples | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hyperscale Providers | Massive global networks offering everything from basic compute to advanced AI. | Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP) | Global enterprises, big SaaS platforms, and large high-traffic apps needing worldwide reach. |
| Niche or Specialized Providers | Targeted services optimized for performance or simplicity. | DigitalOcean, Linode, Vultr | Game studios, agencies, low-latency traders looking for simpler solutions. |
| Open-Source Based Providers | Customizable clouds built on open-source to allow clients maximum freedom and control of their data. | Sharktech Cloud, OVHcloud, Limestone Networks | Organizations focusing on cost optimization, avoiding vendor lock-in, or hybrid/multi-cloud strategies. |
| Private Cloud / On-Prem Support | Platforms for building and managing large in-house or hybrid infrastructure setups. | VMware Cloud, Red Hat OpenShift, Virtuozzo | Regulated industries, legacy infrastructure, or organizations that are not allowed to store data off-prem. |
Benefits of Using a Cloud Service Provider
Cloud service providers offer technical and operational advantages that are difficult for most businesses to match with on-premise infrastructure. These benefits help organizations run more reliably, respond to risks more effectively, and meet growing security and compliance demands.
1. Reliable Infrastructure
Cloud providers maintain large-scale data centers designed for uptime, redundancy, and fault tolerance. This helps reduce the risk of downtime and keeps systems available during peak traffic or unexpected failures.
2. Faster Deployment
Provisioning cloud resources is usually a matter of minutes, not weeks. This gives teams the ability to launch new environments, test tools, or respond to changing needs without being held back by hardware delays.
3. Built-In Security Protections
Cloud providers invest in up-to-date security controls, including firewalls, intrusion detection, and encryption at rest and in transit. Many also offer security monitoring and automated patching to reduce the burden on internal teams.
4. Compliance Tools and Documentation
Providers often support common compliance frameworks, like HIPAA, GDPR, SOC 2, or ISO 27001, with tools that make it easier to meet requirements. This is especially valuable for businesses operating in regulated industries.
5. Scalable Resources
From compute to storage, resources can be adjusted in real time to meet demand. Whether you’re running a data-heavy application or spinning up a temporary workload, scalability helps manage costs and avoid bottlenecks.
6. Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Support
Many providers offer hybrid capabilities, allowing businesses to extend on-premise systems into the cloud or distribute workloads across multiple platforms. This flexibility supports integration, performance, and risk management.
Why Business Leaders Opt for Leading Cloud Providers
Cloud technology isn’t just an IT decision; it’s a strategic one. Business leaders increasingly see cloud services as a way to move faster, stay competitive, and plan with more flexibility.
Here’s how today’s top cloud computing providers contribute to overall business goals:
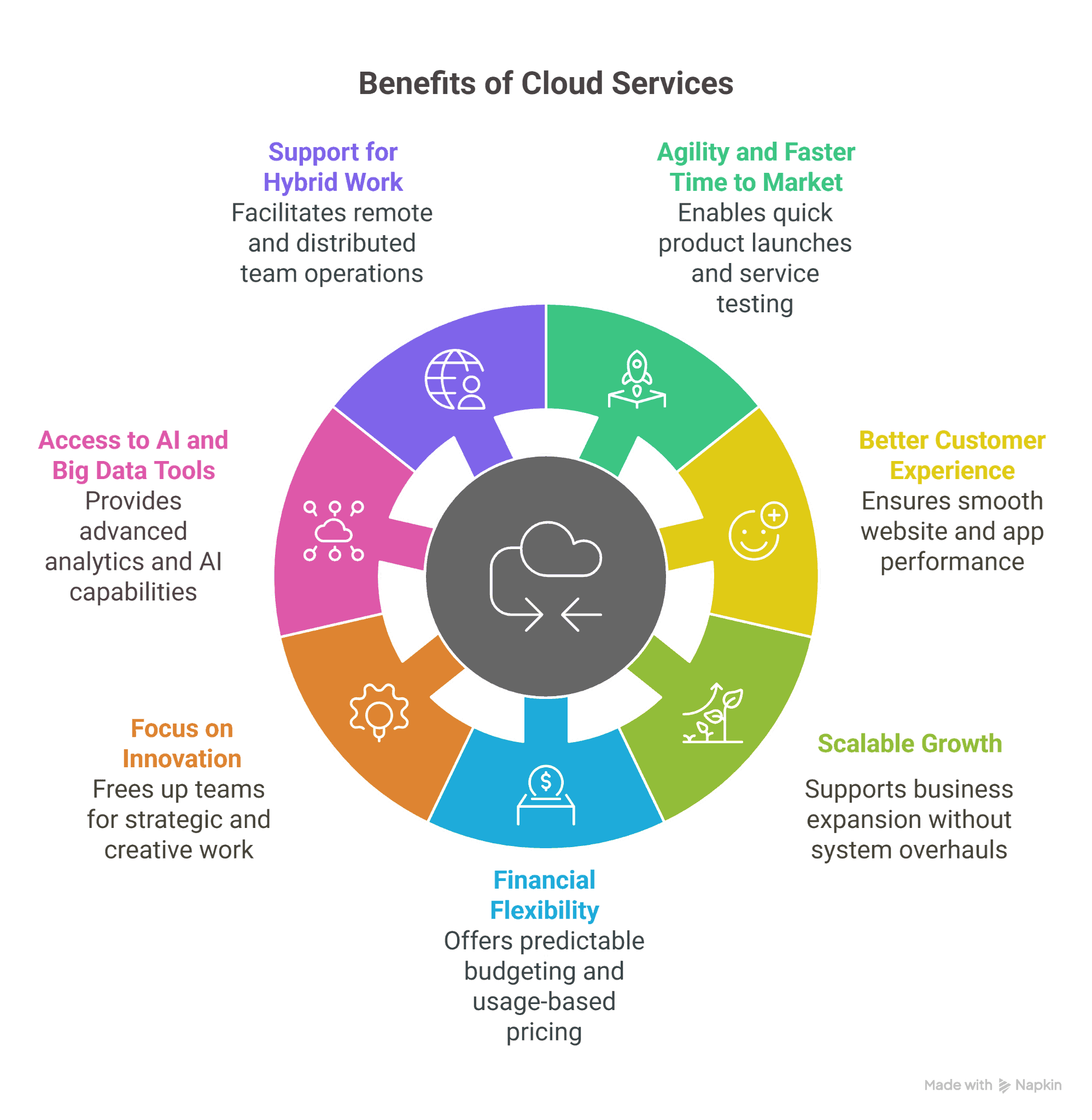
1. Agility and Faster Time to Market
Launching new products, testing services, or responding to customer needs becomes easier when your infrastructure is flexible. Businesses can act on ideas quickly without being delayed by hardware or internal IT capacity.
2. Better Customer Experience
Cloud services help keep websites, apps, and services running smoothly. Fewer outages, faster load times, and consistent performance lead to a better experience for customers and end users.
3. Scalable Growth
Cloud infrastructure scales with your business. Whether you’re growing your customer base or entering a new region, you can expand operations without needing to overhaul your systems.
4. Financial Flexibility
Cloud spending is typically operational rather than capital. This allows for more predictable budgeting, usage-based pricing, and fewer long-term commitments compared to large infrastructure purchases.
5. Focus on Innovation
When your team isn’t managing physical infrastructure, they can focus more on strategy, product development, and process improvement. Cloud services free up time and energy for the work that moves the business forward.
6. Access to AI and Big Data Tools
Many cloud providers offer built-in tools for data analytics, machine learning, and AI model deployment. These capabilities allow businesses to explore automation, gain deeper insights, and make more data-informed decisions—without having to build and maintain those systems in-house.
7. Support for Hybrid Work
Because cloud tools are accessible from anywhere, they make it easier to support remote teams, distributed offices, and hybrid operations. This helps attract talent, keep teams productive, and maintain business continuity.
Challenges of Using a Cloud Service Provider
94% of organizations experience some level of buyer’s remorse with their hyperscaler contract. While cloud service providers offer a wide range of benefits, there are also challenges that come with relying on third-party infrastructure. These aren’t reasons to avoid cloud services, but they are important considerations when planning, budgeting, or choosing a provider.
1. Cost Visibility and Management
Nearly 70% of companies pay for cloud capacity that they are not using, according to a recent study. Cloud pricing can be complex, especially with larger providers that charge based on usage, bandwidth, region, and service tiers. It’s easy for costs to creep up if workloads aren’t monitored closely. Some businesses find it difficult to forecast spending without dedicated tools or internal expertise.
2. Vendor Lock-In
Moving from one cloud provider to another isn’t always simple. Proprietary technologies, platform-specific tools, or deeply integrated services can make switching costly or time-consuming. This is why some organizations prioritize open standards (like OpenStack) or multi-cloud strategies early on.
3. Limited Control
Cloud services abstract away the hardware and infrastructure layer. While this reduces operational burden, it can also limit your ability to fine-tune certain configurations or troubleshoot performance issues directly.
4. Single Vendor Security
While big cloud providers continuously invest in security, the larger the surface, the more difficult it is to protect it. Businesses that work with hyperscalers have to trust a single vendor with all their data and hope that a breach or a data leak won’t occur. That, unfortunately, is not always the case.
More IT insights to explore: |
5. Data Residency and Compliance Complexity
Depending on your industry or region, you may have to comply with data residency requirements, rules about where your data can be stored or processed. Not all providers offer the same flexibility when it comes to data location or compliance support.
6. Support Experience Can Vary
While many providers offer support, the quality, responsiveness, and personalization can vary widely. Some businesses may find themselves navigating ticket systems or documentation instead of speaking with a support rep who understands their environment.
Tips for Finding the Top Cloud Service Provider for Your Needs
Choosing a cloud service provider isn’t about finding the “best” provider overall—it’s about finding the right one for your specific needs. Here are a few things to consider as you explore your options:
- Start with your priorities. Do you need speed, support, pricing predictability, data control, or specific compliance support? Different providers excel in different areas.
- Check pricing transparency. Look for a provider with a pricing model you can understand. Pay attention to hidden costs like bandwidth, storage tiers, or support levels.
- Evaluate support and responsiveness. Will you be relying on a ticketing system or getting help from a real person who understands your setup? This can matter more than you think—especially in high-stakes situations.
- Consider your technical flexibility. Some businesses want full control over their environment. Others prefer a provider that handles everything. Make sure the platform matches your internal capabilities.
- Think about portability. If avoiding vendor lock-in is important to you, look at providers that use open standards or make it easy to move workloads in the future.
- Match the provider to your stage of growth. Hyperscalers might offer broad tools, but they may feel overwhelming for smaller teams. Specialized providers can be a better fit for businesses that want more focus and fewer surprises.
Finding the Best Cloud Service Provider Starts with Fit, Not Size
Whether you’re leaning toward a global platform, a specialized provider, or an open source-based approach, the most important thing is finding a partner that fits your priorities, infrastructure, and long-term business goals.
If you’re exploring alternatives to the large hyperscalers and want more visibility, flexibility, or support, providers like Sharktech Cloud offer a different approach.
Built on OpenStack infrastructure and focused on creating strong, personalized customer relationships, Sharktech is an option for businesses that value control, transparency, and direct access to the people behind their cloud environment.
No matter where you are in your cloud journey, choosing the right provider starts with asking the right questions and staying focused on what matters most to your business. Contact us today.




More to Read
The OpenStack Public Cloud Complexity Problem (And Why It’s Costing You)
Choosing the right cloud platform today is akin to trying to pick a needle
Oct
Make Growth and Security Part of Your Public Cloud Management Strategy
Managing today’s cloud infrastructure is no longer just about spinning up servers or
Sep
Leading Cloud Service Providers Explained: Types, Benefits, and How to Choose
94% of businesses now use a cloud solution in some form. Whether it’s
Aug
What is Public Cloud? A Simple Guide For Businesses
What is public cloud? It’s a model of cloud computing where infrastructure and
Jul
What is Cloud Migration? A Practical Guide for Modern Businesses
What is cloud migration? It’s the process of moving digital assets—like data, applications,
Jul
Why Some Businesses Choose Self-Managed Cloud Instead
Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses deploy, manage, and scale their digital infrastructure.
Apr